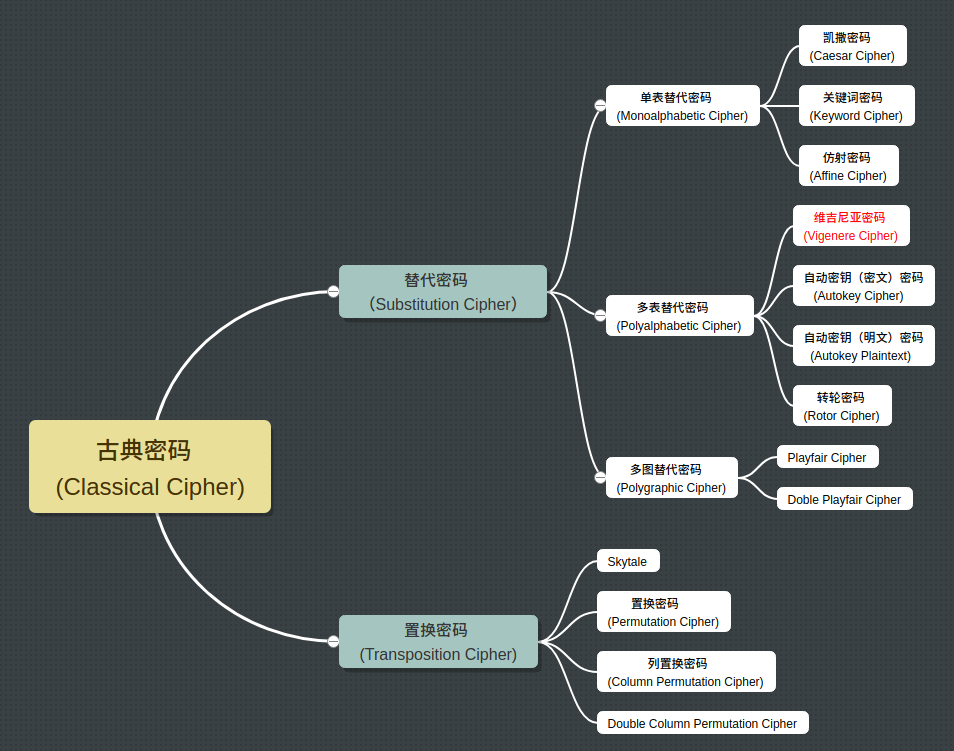
替代密码原理:首先构造一个或多个密文字母表,然后用密文字母表中的字母或字母组来代替明文字母或字母组,各字母或字母组的相对位置不变,但其本身改变了。这样编成的密码称为代替密码。按替代所使用的密文字母表的个数可将代替密码分为单表替代密码和多表替代密码。Vigenere Cipher属于多表替代密码。
Vigenere Cipher数学表达式:
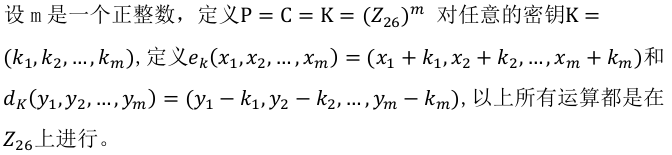
Vigenere Cipher加密/解密原理:在一个具有密钥字长度为m的Vigenere Cipher中,一个字母可以被映射为m个字母中的某一个(假定密钥字包含m个不同的字母)。Vigenere Cipher使用一个词组作为密钥,密钥中的每一个字母确定一个代替表,每一个密钥字母用来加密一个明文字母。等所有密钥字母都使用玩后,密钥再循环使用。Vigenere Cipher的替代规则是用明文字母在Vigenere方阵中的列和密钥字母在Vigenere方阵中的行的交点处的字母来代替该明文字母。其解密就是利用Vigenere Table进行反替代。
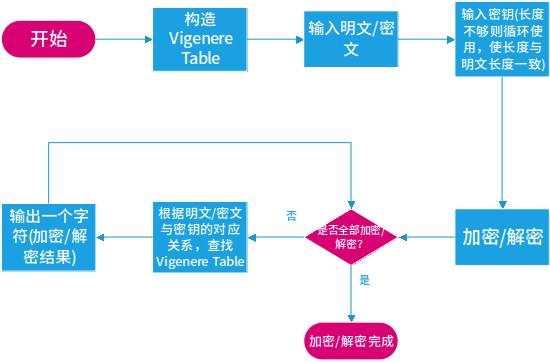
程序思路:要实现对Vigenere Cipher,关键是找到对应关系。因此,其中最重要的一项工作是构造Vigenere Table,之后便可根据密钥与明文一一对应的关系在表中找对应的字符。假定密钥确定的是行替代表,那么密钥所确定的行和明文所确定的列的交叉位置处的字符,即为一个明文字符加密得到的密文字符。对于解密过程则与加密过程相反,由密钥先确定一个替代表(假定密钥确定的行替代表),然后在该表中找到密文字符,密文字符所在列对应的字符即为明文。这里还需要注意的是密钥是循环使用的,密钥长度与明文一致。
程序框图:
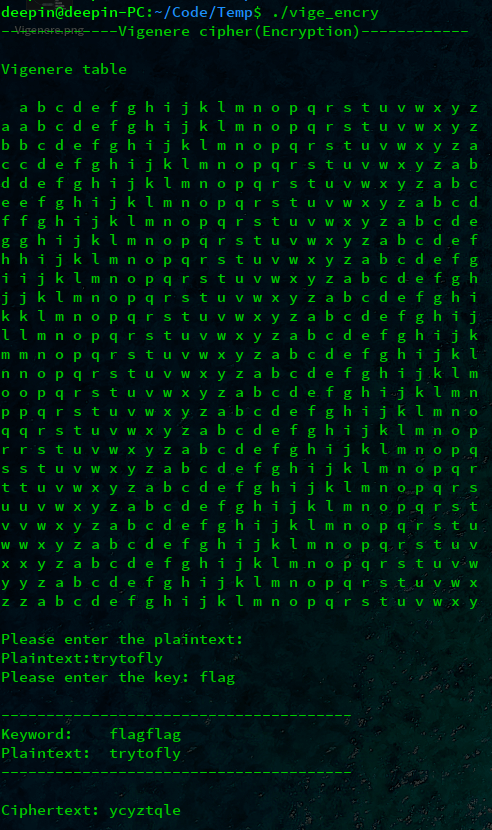
加密代码实现:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 |
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <unistd.h> using namespace std; int Check(string s) { //检查输入的字符串是否为纯英文 int i = 0; while (s[i] != '\0') { if (!((s[i] >= 'a'&&s[i] <= 'z') || (s[i] >= 'A'&&s[i] <= 'Z'))) { cout << "Error!Please enter again!" << endl; sleep(1); return 1; } i++; } return 0; } char(*vigenereTable(char(&list)[26][26]))[26]{ //返回二维数组 int i, j, k; char ch; for (i = 0; i < 26; i++) { for (j = 0; j < 26; j++) { k = 'a' + (i + j) % 26; ch = k; list[i][j] = ch; } } cout << " a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z" << endl; for (i = 0; i < 26; i++) { cout << list[0][i] << " "; for (j = 0; j < 26; j++) { cout << list[i][j] << " "; } cout << endl; } cout << endl; return list; } int main(){ int m, n; int i = 0; int j = 0; int flag = 0; char(*list)[26]; char list1[26][26] = { 0 }; char cipher[26][26] = { 0 }; string key, st; string rule(50, '\0'); do { fflush(stdin); cout << "-------------Vigenere cipher(Encryption)------------" << endl; cout << endl << "Vigenere table" << endl << endl; list = vigenereTable(list1); cout << "Please enter the plaintext:" << endl; cout << "Plaintext:"; cin >> st; flag = Check(st); } while (flag); do { //输入key fflush(stdin); cout << "Please enter the key: "; cin >> key; flag = Check(key); } while (flag); j = 0; for (i = 0; i < st.length(); i++) { j = j % key.length(); rule[i] = key[j]; j++; } rule[i] = '\0'; cout << endl; cout << "---------------------------------------" << endl; cout << "Keyword: " << rule << endl; cout << "Plaintext: " << st << endl; cout << "---------------------------------------" << endl << endl; cout << "Ciphertext: "; for (i = 0; i < st.length(); i++) { m = rule[i] - 'a'; n = st[i] - 'a'; cout << list[n][m]; } cout << endl << endl; return 0; } |
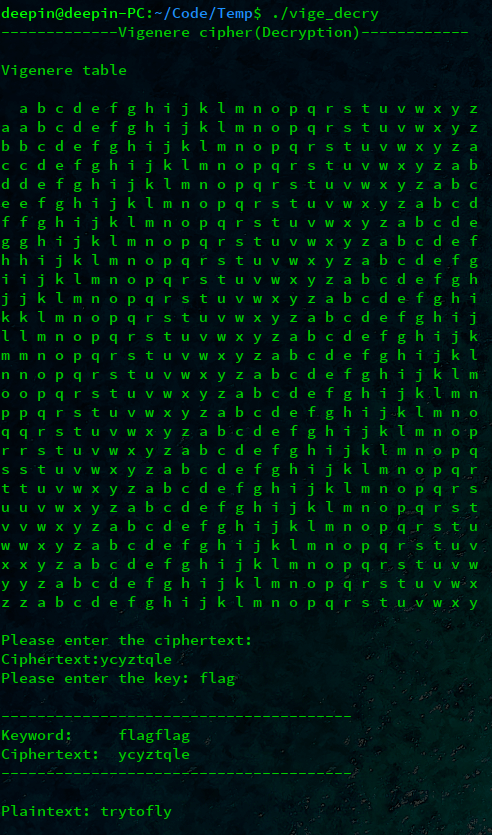
解密代码实现:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 |
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <unistd.h> using namespace std; int Check(string s) { //检查输入的字符串是否为纯英文 int i = 0; while (s[i] != '\0') { if (!((s[i] >= 'a'&&s[i] <= 'z') || (s[i] >= 'A'&&s[i] <= 'Z'))) { cout << "Error!Please enter again!" << endl; sleep(1); return 1; } i++; } return 0; } char(*vigenereTable(char(&list)[26][26]))[26]{ //打印Vigenere表(返回二维数组) int i, j, k; char ch; for (i = 0; i < 26; i++) { for (j = 0; j < 26; j++) { k = 'a' + (i + j) % 26; ch = k; list[i][j] = ch; } } cout << " a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z" << endl; for (i = 0; i < 26; i++) { cout << list[0][i] << " "; for (j = 0; j < 26; j++) { cout << list[i][j] << " "; } cout << endl; } cout << endl; return list; } int main(){ int m, n; int i = 0; int j = 0; int flag = 0; char(*list)[26]; char list1[26][26] = { 0 }; char cipher[26][26] = { 0 }; char plain; string key, st; string rule(50, '\0'); do { fflush(stdin); cout << "-------------Vigenere cipher(Decryption)------------" << endl; cout << endl << "Vigenere table" << endl << endl; list = vigenereTable(list1); cout << "Please enter the ciphertext:" << endl; cout << "Ciphertext:"; cin >> st; flag = Check(st); } while (flag); do { //输入key fflush(stdin); cout << "Please enter the key: "; cin >> key; flag = Check(key); } while (flag); j = 0; for (i = 0; i < st.length(); i++) { j = j % key.length(); rule[i] = key[j]; j++; } rule[i] = '\0'; cout << endl; cout << "---------------------------------------" << endl; cout << "Keyword: " << rule << endl; cout << "Ciphertext: " << st << endl; cout << "---------------------------------------" << endl << endl; cout << "Plaintext: "; //以下是解密关键代码 for (i = 0; i < st.length(); i++) { m = rule[i] - 'a'; for (j = 0; j < 26; j++) { if (list[j][m] == st[i]) break; } n = 'a' + j; plain = n; cout << plain; } cout << endl << endl; } |
思考:
1. Vigenere密码的原理是什么?
答:Vigenere是多表替代,首先构造多个密文字母表,然后用密文字母表中的字母来代替明文字母,明文中的每一个字母都有多种可能的字母来代替。Vigenere密码的代替规则是用明文字母在Vigenere方阵中的列和密钥字母在Vigenere方阵中的行的交叉点处的字母来代替该明文字母。
2. Vigenere密码的主要缺陷有哪些?
答:Vigenere密码使用循环的密钥进行加密。如果两个相同的明文段加密成两个相同的密文段,它们的位置间距假设为δ,则δ=0(mod m)。反过来,如果在密文中观察到两个相同的长度至少为3的密文段,则他们对应了相同的明文串,由此根据两个相同密文段间隔的距离可猜测出密钥长度,这给破译者带来了很大的方便。
3. 对Vigenere密码的分析方法主要思想?
答:Kasiski测试法:搜索长度至少为3的相同密文段,记下其离起始点的那个密文段的距离假如得到如下几个距离𝛿1, 𝛿2,…,那么,可以猜测m为这些𝛿𝑖的最大公因子的因子。
4. 对Vigenere密码的改进方法是什么?
答:增加密钥长度,减少密钥的循环使用。
(编译运行环境:g++ [Debian 7.3.0-19] 7.3.0)























说点什么